Hello friends, we meet again for our journey of learning Java. Today, we are gonna learn something very fruitful and easy. Hope you all are excited and ready. I would recommend you guys to go through the HashSet article which goes over hashing and what sets are actually as this topic has some of its features. So, What's the wait? Let's start! Continuing our example used in HashSet and reusing it here. Suppose you guys are given the task of storing car names (yes, I love cars :p). Now, how would you store it? This question has already been answered by our HashSet article. The new problem here is, we need to store the names in a naturally sorted manner. As we have a set of String, we need to sort them alphabetically. How to do that?
TreeSet
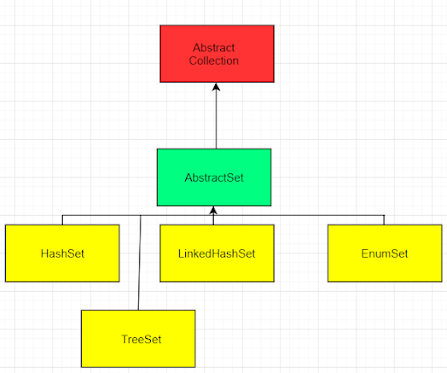
Working of TreeSet in Java
TreeSet is essentially a Red-Black Tree implementation of a self-balancing binary search tree. As a result, operations such as adding, removing, and searching require O(log(N)) time. The reason for this is that in a self-balancing tree, the height of the tree is guaranteed to be O(log(N)) for all operations.As a result, this is regarded as one of the most efficient data structures for storing and processing large amounts of sorted data. Printing N elements in sorted order, on the other hand, takes O(N) time.
Code:
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class MyHashSet {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Set<String> myCarSet = new TreeSet<>();
myCarSet.add("BMW M3");
myCarSet.add("Audi A8");
myCarSet.add("Mercedes Q3");
myCarSet.add("Bugatti veyron");
myCarSet.add("Ferrari spider");
myCarSet.forEach(a -> System.out.print(a+" "));
System.out.println("Traversal completed!");
if(myCarSet.contains("BMW M3")) System.out.println("Yes! BMW hai");
myCarSet.remove("BMW M3");
System.out.println("Traversal started!");
myCarSet.forEach(a -> System.out.print(a + " "));
System.out.println("Traversal completed!");
}
}
Output:
As you all can see, the output is in sorted way.Now, let us see some important points of TreeSet and some advantages and disadvantages.Important points:
- Like HashSet, the Java TreeSet class only has unique items.
- The access and retrieval speeds for the Java TreeSet class are quite quick.
- Null elements are not allowed in the Java TreeSet class.
- The TreeSet class in Java isn't synchronized.
- The TreeSet class in Java keeps ascending/natural order.
I know you guys are now comfortable with TreeSet. but, I will list down 1-2 questions and it's answers which can be useful for you all.What is Natural Ordering in TreeSet Java?
- The ordering suggested by the implementation of the Comparable interface by the objects in the TreeSet is known as "natural" ordering. RBTree must be able to determine which item is smaller than another, and there are two approaches to provide this logic to the RB Tree implementation:
- In the class(es) used as TreeSet objects, we must implement the Comparable interface.
- Provide an implementation of the Comparator that performs comparisons outside of the class.
Why do we need TreeSet when we already had SortedSet in Java?
- TreeSet is the class that implements the sortedSet interface. We all know that we can't construct interface objects in Java. The concrete class that implements the interface must meet the interface's contract, which means it must implement all of the interface's methods. One such implementation is TreeSet.
This is what TreeSet is used for. It is similar to HashSet, but keeps the elements in sorted manner. The sorting is done on the basis on natural ordering by default. You can also provide a comparator explicitly in the constructor so that the sorting can be done on that basis.
- How does get() method of HashMap work in Java? (answer)
- What is the difference between HashSet and HashMap in Java? (answer)
- Difference between ConcurrentHashMap and HashMap in Java? (answer)
- How HashSet internally works in Java? (answer)
- How ConcurrentHashMap internally works in Java? (answer)
- The difference between HashMap and LinkedHashMap in Java? (answer)
- The best way to iterate over HashMap in Java? (answer)
- Difference between HashMap and Hashtable in Java? (answer)
- What is the difference between ArrayList and HashMap in Java? (answer)
- How to sort the HashMap on keys and values in Java? (solution)
- 3 ways to loop over a Map in Java? (example)
- The difference between HashMap and ConcurrentHashMap in Java? (answer)
- What is the difference between ArrayList and HashMap? (difference)
- How to convert Map to List in Java? (solution)
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this TreeSet in Java article then please share with your friends and colleagues. If you have any questions or feedback, please ask in comments.P. S. - If you are new to Java and want to learn core Java in depth, you can also checkout these 10 Free Core Java Courses to start with. It contains best free Java courses from Udemy and Coursera for beginners.

No comments:
Post a Comment