Hello guys, if you are creating Microservices then you may know that API Gateway Design Pattern is a pattern that has emerged as a popular solution for managing APIs in a microservices architecture. As the number of services in the architecture increases, it becomes challenging to manage the APIs and handle requests from external clients. To address this challenge, API Gateway Design Pattern provides a single entry point for all the APIs in a microservices architecture. In the past, we have learned about Database Per Microservices, SAGA, CQRS, Event Sourcing, and Circuit-breaker pattern and in this article, we'll discuss the API Gateway Design Pattern in microservices and provide examples of how to implement it.
What is API Gateway Design Pattern in Microservices? With Examples
In this article, you will learn many things about API Gateway, Here's a brief overview and what you can expect to learn in the article about the "API Gateway Design Pattern in Microservices":
- Definition of API Gateway
- Core Features of API Gateway
- Examples of API Gateway
- Use Cases and Best Practices
Through this article, you'll gain a comprehensive understanding of the API Gateway design pattern, its benefits, core features, examples, use cases, and best practices in the context of microservices architecture.
1. What is API Gateway Design Pattern?
The
API Gateway Design Pattern is a design pattern that provides a single
entry point for all the APIs in a microservices architecture. It acts as
a reverse proxy that receives requests from external clients and
forwards them to the appropriate service.
The API Gateway is responsible
for managing the API traffic, handling authentication and
authorization, and aggregating responses from multiple services. Along with SAGA, CQRS, and Event Sourcing, API Gateways is also an important Microservices design pattern and every Java developer should know about it.
2. Examples of API Gateway
Examples of API Gateway implementation in microservices architecture include popular tools like Netflix Zuul, Amazon API Gateway, and Spring Cloud Gateway, which provide robust solutions for building scalable and resilient API Gateway services.
3. Benefits of API Gateway Design Pattern
There are many advantages of using an API Gateway in microservices-based applications, such as centralized control, abstraction of complexity, and improved performance and reliability.
Here are key the benefits offered by the API Gateway Design Pattern :
- Simplified API management: With the API Gateway, all the APIs are managed in a single place, making it easier to monitor, test, and version them.
- Security: The API Gateway can handle authentication and authorization for all the APIs in the architecture, making it easier to enforce security policies.
- Scalability: The API Gateway can distribute the API traffic to multiple instances of the services, making it easier to scale the services horizontally.
- Reduced complexity: By providing a single entry point for all the APIs, the API Gateway reduces the complexity of the client-side code, making it easier to consume the APIs.
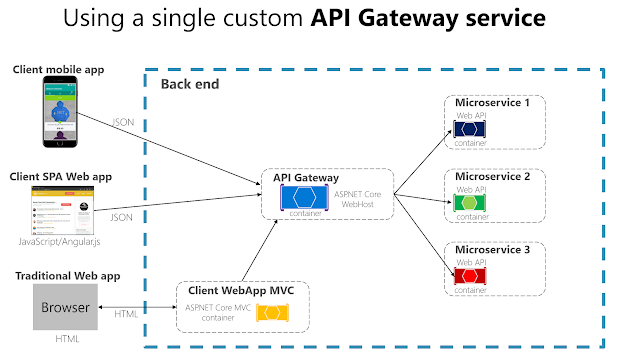
When to use API Gateway? An Example
Let's
consider an example of an e-commerce application that has multiple
microservices, including Product Service, Order Service, and Payment
Service. Each service exposes its APIs, and external clients can consume
these APIs to perform various functions. However, managing these APIs
can be challenging, especially if the application scales and new
services are added.
To address this challenge,
we can use the API Gateway Design Pattern. In this approach, we create
an API Gateway service that acts as a reverse proxy for all the
services' APIs. The API Gateway handles all the requests from external
clients and forwards them to the appropriate service. It also handles
authentication and authorization, caching, and load balancing.
Here's an example of how the API Gateway Design Pattern can be implemented in our e-commerce application:
+-------------------+
| |
| API Gateway |
| |
+-------------------+
|
| Routes requests to appropriate microservices
|
+-------------------+
| |
| Product Service |
| |
+-------------------+
+-------------------+
| |
| Order Service |
| |
+-------------------+
+-------------------+
| |
| Payment Service |
| |
+-------------------+
In
this example, the API Gateway acts as a reverse proxy and routes
requests from external clients to the appropriate microservices. It also
handles authentication and authorization, caching, and load balancing.
The microservices are responsible for performing specific business
functions, such as managing products, orders, and payments.
Let's
take a closer look at how the API Gateway can handle authentication and authorization. Suppose an external client wants to place an order using
the e-commerce application. The client sends a request to the API
Gateway, which then forwards the request to the Order Service.
Before
processing the request, the Order Service needs to ensure that the
client is authorized to place an order. To do this, the Order Service
sends a request to the API Gateway, asking it to validate the client's
credentials.
If the credentials are valid, the API Gateway sends a
response back to the Order Service, indicating that the client is
authorized. The Order Service can then process the order request.
Caching:
Another
important feature of the API Gateway Design Pattern is caching. The API
Gateway can cache responses from the microservices, reducing the number
of requests sent to the microservices and improving the response time.
The API Gateway can use different caching strategies, such as time-based
caching or cache invalidation based on events.
Load Balancing:
The
API Gateway can also perform load balancing, distributing the requests
to multiple instances of the microservices. This improves the
scalability of the microservices and ensures high availability.
Routing:
The
API Gateway can route requests to the appropriate microservices based
on the request's URL, headers, or other parameters. This allows for
flexible routing of requests and enables the implementation of advanced
routing strategies.
Security:
The
API Gateway can also provide an additional layer of security to the
microservices by handling authentication and authorization. The API
Gateway can authenticate clients and authorize them to access specific
microservices based on their role or permissions.
Monitoring and Analytics:
The
API Gateway can also provide monitoring and analytics capabilities for
the microservices. The API Gateway can collect and aggregate metrics,
logs, and traces from the microservices, providing insights into the
system's performance, usage, and errors. This information can be used to
optimize the system and improve the user experience.
API Documentation:
The
API Gateway can also provide API documentation for the microservices,
making it easier for developers to understand the APIs and use them in
their applications. The API Gateway can generate documentation based on
the APIs' specifications, making it easier to keep the documentation
up-to-date.
Conclusion
That's all about what is API Gateway design pattern in Microservices. In
conclusion, the API Gateway Design Pattern is an essential pattern in
microservices architecture that provides a single entry point for all
the APIs in the architecture. It simplifies API management, improves
security, and enables flexible routing, caching, and load balancing.
With the API Gateway, it becomes easier to manage and scale
microservices architecture, improving the overall system's reliability
and performance.
Implementing the API Gateway
Design Pattern requires careful planning and design. It is essential to
identify the services' APIs, determine the appropriate routing and load
balancing strategies, and define the security policies.
However, with
the right implementation, the API Gateway Design Pattern can be an
effective solution for managing APIs in a microservices architecture.
Other Java Microservices articles and tutorials you may like:
- 5 Books to learn Microservice in Java
- Difference between API Gateway and Load Balancer
- 10 courses for Programming/Coding Job Interviews
- 5 Free Spring Framework Courses for Java Developers
- 15 Microservice Interview Question and Answers
- Top 5 Courses to learn Microservice with Spring Boot
- How to create Microservice with Java and Spring
- 10 Free Courses to learn Spring for Beginners
- 5 Courses to Learn Big Data and Apache Spark
- 10 Best Courses to learn Spring in-depth
- 5 Essential Frameworks Every Java developer should learn
- 5 Best Courses to learn Spring MVC for Beginners
- 5 Online Courses to learn Core Java for Free
- 5 Essential Skills to Crack Coding Interviews
- 10 Advanced Spring Boot Courses for Java Programmers
- Top 5 Java design patterns courses for experienced Java devs
- 10 Free Spring Boot Tutorials and Courses for Java Devs
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this Event Sourcing design pattern and when and how to use it then please share them with your friends and colleagues. If you have any questions, feedback, or other fee courses to add to this list, please feel free to suggest.
P. S. - If
you want to learn more about Microservice Architecture and solutions
from scratch and looking for free resources then I highly recommend you
to check out my post about 7 free Microservice courses. It contains free Udemy and Coursera and courses to learn Microservice architecture from scratch.


No comments:
Post a Comment