Coding problems are an integral part of any programming job interviews, and Java development interviews are no exception. I would even suggest you should never hire anyone without testing their coding skill, but coding is also an art, and more often than a good coder is also an excellent developer. If you look at tech giants like Amazon, Facebook, and Google they thoroughly test the coding skill of any developer they hire, notably Amazon who first send online coding exercises to filter Java programmers who can code from those who can't code. This online test usually gives you requirements and ask you to write a program in a limited time, usually 2 to 3 hours. The application should meet the output provided by the exercise itself. These type of tasks are very tough to crack if you don't have excellent coding skill.
Btw, the most crucial question is how do you develop that kind of coding skill in the first place? Well, things always start small, and if you pay attention, there are many Java job interviews where you would have been asked to write small programs.
They are simple, but yet they give a good indication of the coding skill of prospective candidates. They are usually preferred by many companies because it often requires 10 to 20 minutes to write the solution and discuss them.
In this list, I am going to share 50 of such small programs from Java Programming interviews. These programs are from various Data Structure and Algorithm topics like an array, string, linked list, binary tree, etc.
Btw, the most crucial question is how do you develop that kind of coding skill in the first place? Well, things always start small, and if you pay attention, there are many Java job interviews where you would have been asked to write small programs.
They are simple, but yet they give a good indication of the coding skill of prospective candidates. They are usually preferred by many companies because it often requires 10 to 20 minutes to write the solution and discuss them.
In this list, I am going to share 50 of such small programs from Java Programming interviews. These programs are from various Data Structure and Algorithm topics like an array, string, linked list, binary tree, etc.
You can practice solving these 50 Java programs from coding interviews to not just level up your coding skills but also to learn data structure, algorithms, bit manipulation and Software design concepts in details.
I have also updated the article to include few System design questions on the list because System design is getting more popular every passing day and if you are an experienced developer with 2 to 3 years of experience or senior developer with 5 to 10 years of experience then you can expect few System design questions on interview too.
Here is also a Big O Notation cheat sheet which you can revise quickly as they are quite important for coding interviews, especially if interviewer ask about time and space performance for any algorithms or ask you to improve your algorithms:
Here is also a Big O Notation cheat sheet which you can revise quickly as they are quite important for coding interviews, especially if interviewer ask about time and space performance for any algorithms or ask you to improve your algorithms:
Top 50 Java Programs from Coding Interviews
Here is a big list of Java programs for Job Interviews. As I said, it includes questions from problem-solving, linked list, array, string, matrix, bitwise operators and other miscellaneous parts of programming. Once you are gone through these questions, you can handle a good number of questions on real Job interviews.1. Fibonacci series (solution)
Write a simple Java program which will print Fibonacci series, e.g. 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 ... . up to a given number. We prepare for cross questions like using iteration over recursion and how to optimize the solution using caching and memoization.
2. A prime number (solution)
Write a Java program to check if a given number is prime or not. Remember, a prime number is a number which is not divisible by any other number, e.g. 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, etc. Be prepared for cross, e.g. checking till the square root of a number, etc.
3. String Palindrome (solution)
You need to write a simple Java program to check if a given String is palindrome or not. A Palindrome is a String which is equal to the reverse of itself, e.g., "Bob" is a palindrome because of the reverse of "Bob" is also "Bob."
Though be prepared with both recursive and iterative solution of this problem. The interviewer may ask you to solve without using any library method, e.g. indexOf() or subString() so be prepared for that.
4. Integer Palindrome (solution)
This is generally asked as follow-up or alternative of the previous program. This time you need to check if given Integer is palindrome or not. An integer is called palindrome if it's equal to its reverse, e.g. 1001 is a palindrome, but 1234 is not because the reverse of 1234 is 4321 which is not equal to 1234. You can use divide by 10 to reduce the number and modulus 10 to get the last digit. This trick is used to solve this problem.
5. Armstrong number (solution)
A number is called an Armstrong number if it is equal to the cube of its every digit. For example, 153 is an Armstrong number because of 153= 1+ 125+27, which is equal to 1^3+5^3+3^3. You need to write a program to check if the given number is Armstrong number or not.
6. Avoiding deadlock in Java (solution)
This is one of the interesting programs from Java Interviews, mostly asked to 2 to 3 years of experienced programmers or higher. The interviewer simply asked you to write code where a resource is accessed by multiple threads.
4. Integer Palindrome (solution)
This is generally asked as follow-up or alternative of the previous program. This time you need to check if given Integer is palindrome or not. An integer is called palindrome if it's equal to its reverse, e.g. 1001 is a palindrome, but 1234 is not because the reverse of 1234 is 4321 which is not equal to 1234. You can use divide by 10 to reduce the number and modulus 10 to get the last digit. This trick is used to solve this problem.
5. Armstrong number (solution)
A number is called an Armstrong number if it is equal to the cube of its every digit. For example, 153 is an Armstrong number because of 153= 1+ 125+27, which is equal to 1^3+5^3+3^3. You need to write a program to check if the given number is Armstrong number or not.
6. Avoiding deadlock in Java (solution)
This is one of the interesting programs from Java Interviews, mostly asked to 2 to 3 years of experienced programmers or higher. The interviewer simply asked you to write code where a resource is accessed by multiple threads.
You need to write code in such a way that no deadlock should occur. The trick to solving this problem is acquiring resources in order and release them in reverse order, e.g. first acquire resource R1 and only if you have got R1 to go for R2. This way, you can avoid deadlock.
7. Factorial (solution)
This is one of the simplest programs you can expect in interviews. It is generally asked to see if you can code or not. Sometimes interviewer may also ask about changing a recursive solution to iterative one or vice-versa.
8. Reverse a String (solution)
This problem is similar to the String Palindrome problem we have discussed above. If you can solve that problem, you can solve this as well. You can use indexOf() or substring() to reverse a String or alternatively, convert the problem to reverse an array by operating on character array instead of String.
7. Factorial (solution)
This is one of the simplest programs you can expect in interviews. It is generally asked to see if you can code or not. Sometimes interviewer may also ask about changing a recursive solution to iterative one or vice-versa.
8. Reverse a String (solution)
This problem is similar to the String Palindrome problem we have discussed above. If you can solve that problem, you can solve this as well. You can use indexOf() or substring() to reverse a String or alternatively, convert the problem to reverse an array by operating on character array instead of String.
9. Remove duplicates from an array (solution)
Write a program to remove duplicates from an array in Java without using the Java Collection API. The array can be an array of String, Integer or Character, your solution should be independent of the type of array. If you want to practice more array-based questions, then see this list of top 30 array interview questions from Java interviews.
In this exercise you will be asked to print various kind of patterns like printing star patterns or printing pyramid patterns. Another common coding problem is printing left and right triangle of stars or numbers which require use of nested loops in Java.
11. Print repeated characters of String? (solution)
11. Print repeated characters of String? (solution)
This is another common coding interview questions where you need to print repeated characters like AAABBCCCC. You can solve this coding problem to learn about how to use loops and how to use break and continue to control the loop in Java.
12. GCD of two numbers (solution)
12. GCD of two numbers (solution)
GCD also known as Greatest Common divisor is a number which can fully divide the given two numbers. You can solve this problem either with brute force algorithms or you can also use Euclid's algorithm to find the GCD of two given numbers.
13. The square root of a number (solution)
You need to write a program to calculate the square root of a number without using the Math.sqrt() function of JDK. You need to write your logic and method to calculate the square root. You can though use the popular algorithm, like Newton's method.
14. Reverse array in place (solution)
You need to write a program to calculate the square root of a number without using the Math.sqrt() function of JDK. You need to write your logic and method to calculate the square root. You can though use the popular algorithm, like Newton's method.
14. Reverse array in place (solution)
This one is my favorite coding exercise and I have asked this question multiple time on coding interviews. In place algorithms are quite useful while dealing with large data sets, for example if you have to reverse an array with 1 million objects then its very expensive to create another array of same size, at that time, this in place algorithm is a better choice.
15. Reverse words of a sentence (solution)
16. Leap year (solution)
17. Binary search (solution)
18. String Anagram (solution)
Write a program to check if two given String is Anagram of each other. Your function should return true if two Strings are Anagram, false otherwise. A string is said to be an anagram if it contains the same characters and same length, but in a different order, e.g. army and Mary are anagrams. You can ignore cases for this problem, but you should clarify that from your interview.
19. Design a Vending Machine (solution)
This one of the popular OOAD (object-oriented analysis and design) question from Java Interviews. You will be given 3 hours to design and code a vending machine satisfying some of the business requirements. You also need to write unit tests to prove your code satisfy those requirements. You can see this article for more object-oriented analysis questions.
20. Reverse a number (solution)
21. The first non-repeated character of String (solution)
22. Finding Middle element of linked list in one pass (solution)
23. Pre-order traversal (solution)
24. Pre-order traversal without recursion (solution)
25. In order traversal (solution)
26. In order traversal without recursion (solution)
27. Post-order traversal (solution)
28. Postorder traversal without recursion (solution)
29. Print all leaves of a binary tree (solution)
30. Sort array using quicksort (solution)
You need to write a Java program to sort an array of integers using a quick sort algorithm. You cannot use any library method, e.g. JDK or a third party library, which means, you need to first implement the quicksort algorithm and then sort the array.
31. Insertion sort (solution)
Write a program to implement the insertion sort algorithm in Java. The program should take an unsorted array and sort it using insertion sort algorithm Also explain the best case and worst case time and space complexity of the Insertion sort algorithm.
32. Bubble sort (solution)
Write a program to implement the bubble sort algorithm in Java. You can use basic operators and functions, but sorting functions from Java API is not allowed.
33. Transpose a matrix (solution)
34. Print all permutations of String (solution)
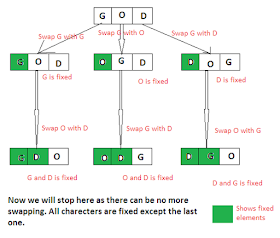
Write a Java program to print all permutations of a given String. For example, if given String is "GOD" then your program should print all 6 permutations of this string, e.g. "GOD," "OGD," "DOG," "GDO," "ODG," and "DGO."
35. Reverse a String in place (solution)
36. Adding two matrices in Java (solution)
37. Matrix multiplication (solution)
38. Removal all white space from String (solution)
39. Reverse a linked list (solution)
Write a program to reverse a singly linked list in Java. You can use iteration and recursion to solve this problem, but you should reverse a linked list in place.
40. Find the length of the linked list (solution)
Just write a program in Java to find the length of a singly linked list in one pass, i.e. in just one iteration of a singly linked list.
41. Check if a linked list has a loop (solution)
Write a program to check if given linked list has a loop or not. Sometimes a linked list get corrupt, and two nodes point to the same node, which forms the loop or cycle in the linked list.
42. Find the start of loop in a linked list (solution)
15. Reverse words of a sentence (solution)
16. Leap year (solution)
17. Binary search (solution)
18. String Anagram (solution)
Write a program to check if two given String is Anagram of each other. Your function should return true if two Strings are Anagram, false otherwise. A string is said to be an anagram if it contains the same characters and same length, but in a different order, e.g. army and Mary are anagrams. You can ignore cases for this problem, but you should clarify that from your interview.
19. Design a Vending Machine (solution)
This one of the popular OOAD (object-oriented analysis and design) question from Java Interviews. You will be given 3 hours to design and code a vending machine satisfying some of the business requirements. You also need to write unit tests to prove your code satisfy those requirements. You can see this article for more object-oriented analysis questions.
20. Reverse a number (solution)
21. The first non-repeated character of String (solution)
22. Finding Middle element of linked list in one pass (solution)
23. Pre-order traversal (solution)
24. Pre-order traversal without recursion (solution)
25. In order traversal (solution)
26. In order traversal without recursion (solution)
27. Post-order traversal (solution)
28. Postorder traversal without recursion (solution)
29. Print all leaves of a binary tree (solution)
30. Sort array using quicksort (solution)
You need to write a Java program to sort an array of integers using a quick sort algorithm. You cannot use any library method, e.g. JDK or a third party library, which means, you need to first implement the quicksort algorithm and then sort the array.
31. Insertion sort (solution)
Write a program to implement the insertion sort algorithm in Java. The program should take an unsorted array and sort it using insertion sort algorithm Also explain the best case and worst case time and space complexity of the Insertion sort algorithm.
32. Bubble sort (solution)
Write a program to implement the bubble sort algorithm in Java. You can use basic operators and functions, but sorting functions from Java API is not allowed.
33. Transpose a matrix (solution)
34. Print all permutations of String (solution)
Write a Java program to print all permutations of a given String. For example, if given String is "GOD" then your program should print all 6 permutations of this string, e.g. "GOD," "OGD," "DOG," "GDO," "ODG," and "DGO."
35. Reverse a String in place (solution)
36. Adding two matrices in Java (solution)
37. Matrix multiplication (solution)
38. Removal all white space from String (solution)
39. Reverse a linked list (solution)
Write a program to reverse a singly linked list in Java. You can use iteration and recursion to solve this problem, but you should reverse a linked list in place.
40. Find the length of the linked list (solution)
Just write a program in Java to find the length of a singly linked list in one pass, i.e. in just one iteration of a singly linked list.
41. Check if a linked list has a loop (solution)
Write a program to check if given linked list has a loop or not. Sometimes a linked list get corrupt, and two nodes point to the same node, which forms the loop or cycle in the linked list.
42. Find the start of loop in a linked list (solution)
This is the extension of previous problem, once you are able to detect a loop in the linked list, the node where you deduct the loop becomes the starting point.
43. Find the middle element of a linked list (solution)
43. Find the middle element of a linked list (solution)
You can find the middle element of a linked list by using two pointer coding interview patterns or slow and fast pointer approach where one pointer will be slow and move one step at a time and other will be fast and move two steps at a time. This way when first pointer will reach the end of the list, the second pointer will be at the middle element of the linked list.
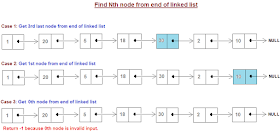
44. Find the 3rd element from the tail linked list (solution)
You need to write a program to find the 3rd element from the tail of a singly linked list. You need to solve this problem without iterating twice. If you want more linked list questions, you can see the article about frequently asked linked list interview questions.
44. Convert a linked list to a binary tree (solution)
It's possible to convert a doubly-linked list to a binary tree, you need to write a Java program which takes a doubly-linked list and returns a binary tree.
45. Sort a linked list (solution)
You need to given an unsorted linked list, and you need to write a program in Java to sort them in ascending order of the values in each node.
46. Iterative Quicksort (solution)
You need to write a Java program to implement quicksort sorting algorithm without recursion. You can use essential JDK classes and programming constructs, but recursion is not allowed.
46. Bucket sort (solution)
This program is increasingly getting popular on Java interview because it sorts a given array in linear time. Though there is a lot of prerequisites, e.g. you must know the maximum value present in the array, it is a very interesting problem from interview point of view.
44. Find the 3rd element from the tail linked list (solution)
You need to write a program to find the 3rd element from the tail of a singly linked list. You need to solve this problem without iterating twice. If you want more linked list questions, you can see the article about frequently asked linked list interview questions.
44. Convert a linked list to a binary tree (solution)
It's possible to convert a doubly-linked list to a binary tree, you need to write a Java program which takes a doubly-linked list and returns a binary tree.
45. Sort a linked list (solution)
You need to given an unsorted linked list, and you need to write a program in Java to sort them in ascending order of the values in each node.
46. Iterative Quicksort (solution)
You need to write a Java program to implement quicksort sorting algorithm without recursion. You can use essential JDK classes and programming constructs, but recursion is not allowed.
46. Bucket sort (solution)
This program is increasingly getting popular on Java interview because it sorts a given array in linear time. Though there is a lot of prerequisites, e.g. you must know the maximum value present in the array, it is a very interesting problem from interview point of view.
You need to write a program to implement a bucket sort algorithm in Java.
47. Counting sort (solution)
This is another problem which is similar to the previous one because counting sort is also a linear sorting algorithm. Just remember that bucket sort, and counting sort are different algorithms, so it's also good to state how they are different.
48. Check if two string rotation of each other
Write a program which accepts two given String and checks if they are the rotation of each. If they then return true otherwise return false. A String is said to be a rotation of other string if they contain same characters and the sequence is rotated across any character, e.g. "dabc" is a rotation of "abcd" but "dbac" is not. If you want to practice more string-based questions, you can also see my list of 20 String-based algorithm questions from Java interviews.
47. Counting sort (solution)
This is another problem which is similar to the previous one because counting sort is also a linear sorting algorithm. Just remember that bucket sort, and counting sort are different algorithms, so it's also good to state how they are different.
48. Check if two string rotation of each other
Write a program which accepts two given String and checks if they are the rotation of each. If they then return true otherwise return false. A String is said to be a rotation of other string if they contain same characters and the sequence is rotated across any character, e.g. "dabc" is a rotation of "abcd" but "dbac" is not. If you want to practice more string-based questions, you can also see my list of 20 String-based algorithm questions from Java interviews.
49. LRU cache in Java (solution)
Write a program to implement an LRU cache in Java. An LRU cache means Least Recently Used Cache which removes the least recently used element if the cache is full. You can use the LinkedHashMap to implement LRU cache in Java.
50. Merge sort (solution)
Implement the merge sort algorithm in Java. You can write a recursive or iterative solution, whichever you like. You also need to explain the time and space complexity for the best, worst, and average case. If you need hint, Merge sort is based on divide and conquer technique, where you divide a big array or list into small parts and then sort them individually and then merge it.
Now, let's see a couple of System deign questions which you can also prepare for programming interviews:
1. Difference between JWT, OAuth, and SAML? (answer)
2. Reverse Proxy and Forward Proxy? (answer)
3. Horizontal scaling and vertical scaling? (answer)
4. Microservices and Monolithic architecture? (Answer)
5. What is Rate Limiter? How does it work? (answer)
6. API Gateway vs Load Balancer? [solution]
7. How does Single Sign On (SSO) works?
(answer)
8. How does Apache Kafka works? why it so fast? (answer)
9. Difference between Kafka, ActiveMQ, and RabbitMQ? (answer)
That's all about top 50 programs from Java interviews. You can practice these Java programs even if you are not preparing for any Job interview. They not only help you to do well on your programming job interviews but also on learning how to code and developing your programming skill and coding sense.
These small programs touch several important areas, e.g. popular data structures like an array, linked list, binary tree, binary search tree, string, etc., popular algorithms, e.g. sieve of the Eratosthenes algorithm for generating primes, the Euclidean algorithm for calculating LCM, and GCF, Fibonacci sequence, printing patterns and so on.
These Java programs also touch base on useful operators like bit-shift and bitwise operators, modulus operators, and others. Overall, you get a good understanding of the Java programming world by practicing these Java programs from coding interviews.
Recommended Resources for Coding Interviews
- 50+ Data Structure and Algorithms Interview Questions
- 20+ Basic Algorithms Questions from Interviews
- 20 System Design Interview Questions
- How to Crack System Design Interview [The Ultimate Guide]
- 10 Dynamic Programming Interview Questions
- 10 Matrix based Coding Problems for Interviews
- 100+ System Design Interview Questions
- 25 Recursion based Coding Interview Questions and Answers
Thanks for reading this article so far, if you like these Java programs, then please share with your friends and colleagues, if you have any question or problem, then please drop a comment.
Also, let me know in comments if any of these Java programs were asked to you on Coding interviews? Or any other programs which is not in the list but asked to you on Java interviews




Nice collection of interview question
ReplyDeleteGood Programmas
ReplyDeleteGood collection
ReplyDeleteDo you know any other books recommended for coding interviews?
ReplyDeleteI used:
ReplyDelete"Cracking the Coding Interview" by Gayle Laakmann McDowell
"TOP 30 Java Interview Coding Tasks" by Matthew Urban
"Elements of Programming Interviews in Java" by Adnan Aziz, Tsung-Hsien Lee, Amit Prakash
"Coding Interview Questions" by Narasimha Karumanchi
nice collection of questions. Thank you.
ReplyDeleteReally helpful ! Thanks !
ReplyDeleteString palindrome is found with error.unable to view it
ReplyDeleteHello @Unknown, can you give more details? you mean you can't see the solution?
ReplyDeleteAh got it, the link is incorrect, I'll correct it.
ReplyDeleteperfect ...thank you,Guys!
ReplyDeleteThanks! for help,guys.
ReplyDeleteVery nice..
ReplyDeleteBut I need a differential and integral problems in java
If any one think about it reply me...
We'll discuss about it😊😊😊
Nice thank you
ReplyDelete🙄🙄🙄 good
ReplyDeleteIt's very much benificial for us
ReplyDeleteMy problem with this type of question is that most of them do not reflect the types of problems you encounter on the job. A good java programmer knows how to perform task needed by the job. A DB centric application will manipulate many data results efficiently. That might mean knowing lists, iterations, or using lombok. A realtime application will be more focused on things like concurrency. I've used Java professionally since it was in beta nad have never had to shift bits.
ReplyDeleteHello Bill, interview and real work is always different. It's part of the culture we have. I think asking these kind of question is to check if people have good fundamental knowledge or not. This is important for engineering a solution rather than just coding. For example, if you know about paging, swap memory, virtual memory you will be better equipped to solve memory related problems of Java application. Just my 2 cent.
ReplyDeleteCan u plzz help me in solving the below pattern-:
ReplyDelete55555
54444
54333
54322
54321
@Unknown, I can give you an hint, use two for loop and a combination of system.out.println() and system.print() to print this pattern
ReplyDelete@Unknown
ReplyDeletepublic static void main(String[] s)
{
int i=55555;
int r=1111;
System.out.println(i);
for(int j=0;j<4;j++)
{
i=i-r;
System.out.println(i);
r=r/10;
}
@Unknown
ReplyDeletepublic static void main(String []args){
String num = "";
for(int i = 5; i>=1; i--){
num += i;
//System.out.print(i);
for(int j = 1; j<=i; j++){
System.out.print(i);
}
if(i != 1){
System.out.print("\n"+num);
}
}
}
5432 is the answer of program
DeleteNum value is 5
Deletewhat are the modifiers applicable in java main method
ReplyDeleteVery helpful this kind of coding to pass in coding test
ReplyDelete*** *
ReplyDelete** **
* ***
Please slove this program
Reverse String .....
ReplyDeletepublic class Reve
{
public static void main(String [] args)
{
String s="hello java";
String s1=" ";
for(int i=s.length()-1;i>=0;i--)
{
s1=s1+s.CharAt();
}
System.out.println("Original String : "+s);
System.out.println("Reverse String : "+s1);
}
}
Can you please add Dynamic Programming Interview questions on this list?
ReplyDelete1st non Repeating character and Binary Search
ReplyDeletewere asked.
Any newsletter would you recommend for coding interview preparation?
ReplyDelete