Many times we need to create backup or copy of tables in databases like
MySQL, Oracle, or PostgreSQL while modifying table schema like adding new
columns, modifying columns, or dropping columns. Since it's always best to have a
backup of a table that can be used in any event. I was looking for an easy way
to create an exact copy or duplicate tables which must be the same in the schema as well
as in data, similar to creating a copy of the folder. Luckily there is an easy SQL
query "CREATE table table_name AS" which allows you to create an exact
copy of the table by executing just one SQL query. Yes, you read it
correctly, no tool is required to create a backup of the table you just need to
execute an SQL query.
This is simply awesome given its importance and the best part of this SQL query is that it works in almost all the databases. I have tested it in MySQL and Oracle but t it should work perfectly fine in other databases like PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and DB2 as well.
Btw, this SQL query tip is in continuation of my earlier SQL query examples like SQL query to find duplicate rows in a table and SQL query to join three tables in MySQL .
This is simply awesome given its importance and the best part of this SQL query is that it works in almost all the databases. I have tested it in MySQL and Oracle but t it should work perfectly fine in other databases like PostgreSQL, SQL Server, and DB2 as well.
Btw, this SQL query tip is in continuation of my earlier SQL query examples like SQL query to find duplicate rows in a table and SQL query to join three tables in MySQL .
How to copy table using SQL query in MySQL? Example
 Now let's see it an action. In this example I am creating exact replica
of table for demonstration. We will use a table called AIRCRAFT which has
3 records and after creating backup of AIRCRAFT table we
will verify both count and records to see if its exact replica of source table
or not. Here is our SQL query to create
backup of table in MySQL without any tool:
Now let's see it an action. In this example I am creating exact replica
of table for demonstration. We will use a table called AIRCRAFT which has
3 records and after creating backup of AIRCRAFT table we
will verify both count and records to see if its exact replica of source table
or not. Here is our SQL query to create
backup of table in MySQL without any tool:
create table table_name as select * from source_table
where table_name is name of backup table and source_table is name of
source table in database. SELECT query example which is
used to fetch data can be a complex query which can fetch data from multiple
table as well.
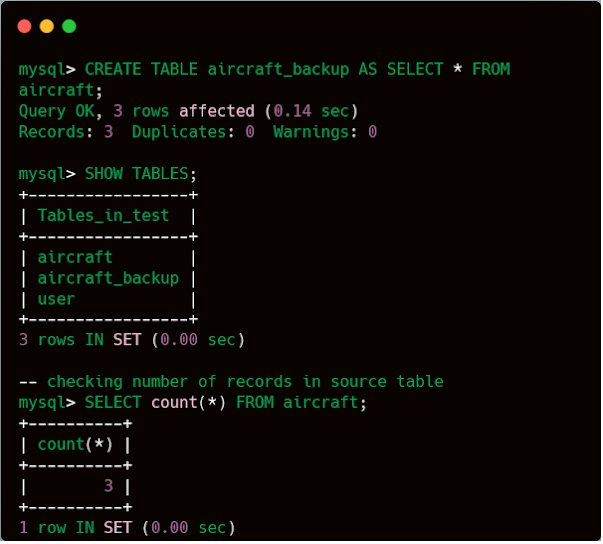
-- showing list of table before
creating backup
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| aircraft |
| user |
+----------------+
2 rows IN SET (0.34 sec)
+----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+----------------+
| aircraft |
| user |
+----------------+
2 rows IN SET (0.34 sec)
-- creating backup of aircraft table
by selecting all data
mysql> CREATE TABLE
aircraft_backup AS SELECT * FROM aircraft;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.14 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
+-----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+-----------------+
| aircraft |
| aircraft_backup |
| user |
+-----------------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.14 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SHOW TABLES;
+-----------------+
| Tables_in_test |
+-----------------+
| aircraft |
| aircraft_backup |
| user |
+-----------------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
-- checking number of records in
source table
mysql> SELECT count(*)
FROM aircraft;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 3 |
+----------+
1 row IN SET (0.00 sec)
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 3 |
+----------+
1 row IN SET (0.00 sec)
-- verifying number of records in
newly created backup table
mysql> SELECT count(*)
FROM aircraft_backup;
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 3 |
+----------+
1 row IN SET (0.00 sec)
+----------+
| count(*) |
+----------+
| 3 |
+----------+
1 row IN SET (0.00 sec)
-- data in original table
mysql> SELECT * FROM aircraft;
+-----+--------+---------------+
| aid | aname | cruisingrange |
+-----+--------+---------------+
| 301 | Boeing | 16000 |
| 302 | Airbus | 10000 |
| 303 | Jet | 8000 |
+-----+--------+---------------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
+-----+--------+---------------+
| aid | aname | cruisingrange |
+-----+--------+---------------+
| 301 | Boeing | 16000 |
| 302 | Airbus | 10000 |
| 303 | Jet | 8000 |
+-----+--------+---------------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
-- data in backup table should be
exactly same with source table
mysql> SELECT * FROM aircraft_backup;
+-----+--------+---------------+
| aid | aname | cruisingrange |
+-----+--------+---------------+
| 301 | Boeing | 16000 |
| 302 | Airbus | 10000 |
| 303 | Jet | 8000 |
+-----+--------+---------------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
+-----+--------+---------------+
| aid | aname | cruisingrange |
+-----+--------+---------------+
| 301 | Boeing | 16000 |
| 302 | Airbus | 10000 |
| 303 | Jet | 8000 |
+-----+--------+---------------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
How to create a table from another table in SQL
creating table from another table in SQL is same as copying table but you have a choice
to either just copy the schema or copy schema and data together. In order to
create SQL table from another table just use following create table SQL query
and replace name of table with exact name you want.
create table destination_table as select * from
source_table;
In order to create table by copying schema from another table without
data use a condition in WHERE clause which always returns false.
mysql> CREATE TABLE
AIRCRAFT_SCHEMA_BACKUP AS SELECT * FROM AIRCRAFT WHERE
3=4;
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SELECT * FROM AIRCRAFT_SCHEMA_BACKUP;
Empty SET (0.00 sec)
mysql> DESCRIBE AIRCRAFT_SCHEMA_BACKUP;
+---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| FIELD | Type | NULL | KEY | DEFAULT | Extra |
+---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| aid | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| aname | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| cruisingrange | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows IN SET (0.06 sec)
Query OK, 0 rows affected (0.11 sec)
Records: 0 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SELECT * FROM AIRCRAFT_SCHEMA_BACKUP;
Empty SET (0.00 sec)
mysql> DESCRIBE AIRCRAFT_SCHEMA_BACKUP;
+---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| FIELD | Type | NULL | KEY | DEFAULT | Extra |
+---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
| aid | int(11) | NO | | NULL | |
| aname | varchar(20) | YES | | NULL | |
| cruisingrange | int(11) | YES | | NULL | |
+---------------+-------------+------+-----+---------+-------+
3 rows IN SET (0.06 sec)
f you want to create a table from another table with data and schema than
just execute above SQL query without WHERE clause.
In case if you don't want your new table to contains all columns and only
few columns from the original table than instead of using select
* just use select column, column etc as shown in below SQL query:
mysql> CREATE TABLE
AIRCRAFT_BK AS SELECT aid,
aname FROM AIRCRAFT;
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.13 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SELECT * FROM AIRCRAFT_BK;
+-----+--------+
| aid | aname |
+-----+--------+
| 301 | Boeing |
| 302 | Airbus |
| 303 | Jet |
+-----+--------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
Query OK, 3 rows affected (0.13 sec)
Records: 3 Duplicates: 0 Warnings: 0
mysql> SELECT * FROM AIRCRAFT_BK;
+-----+--------+
| aid | aname |
+-----+--------+
| 301 | Boeing |
| 302 | Airbus |
| 303 | Jet |
+-----+--------+
3 rows IN SET (0.00 sec)
That's all on creating a backup of table or copying table by using SQL
query. We have seen how to copy tables, how to create table from another table
with data and without data and how to create duplicates of table. You always
have flexibility on choosing columns or data.
Other database and SQL tutorials from Javarevisited









1 comment :
When working with an Oracle database, you may need to create a copy of the table to test or develop your application properly. We have selected the best ways to accomplish different types of table copying in Oracle and provided an accurate description of each method.
https://www.devart.com/dbforge/oracle/studio/oracle-copy-table.html
Post a Comment