Stack and Queue are two of the important data structures in the programming world and have a variety of usage. As opposed to the array and linked list, which are considered primary data structures, they are secondary data structures that can build using an array or linked list. You can use Stack to solve recursive problems and Queue can be used for ordered processing. The difference between Stack and Queue Data structure is also one of the common questions not only in Java interviews but also in C, C++, and other programming job interviews.
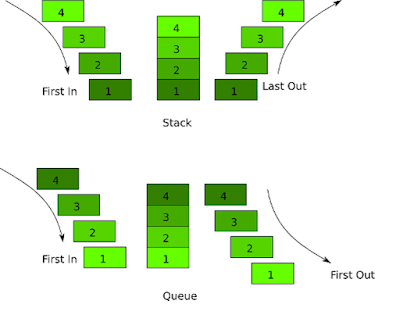
Well, the main difference comes the way these data structures are used, Stack is LIFO (Last In First Out) data structure, which means the item which is inserted last is retrieved first, similar to a stack of plates in a dinner party, where every guest pick up the plate from the top of the stack.
On the other hand Queue data structure literally represent a queue, which is a FIFO (First In First Out) data structure, i.e. object which is first inserted, is first consumed, because insertion and consumption happen at the opposite end of the queue.
When the difference between Stack and Queue is asked in Java Interviews, the interviewer also expects you to be familiar with the Stack and Queue classes from Java Collection Framework.
Well, the main difference comes the way these data structures are used, Stack is LIFO (Last In First Out) data structure, which means the item which is inserted last is retrieved first, similar to a stack of plates in a dinner party, where every guest pick up the plate from the top of the stack.
On the other hand Queue data structure literally represent a queue, which is a FIFO (First In First Out) data structure, i.e. object which is first inserted, is first consumed, because insertion and consumption happen at the opposite end of the queue.
When the difference between Stack and Queue is asked in Java Interviews, the interviewer also expects you to be familiar with the Stack and Queue classes from Java Collection Framework.
Java supports both these data structures and provides a sample implementation of them, by the way, you should also be familiar with implementing Stack and Queue in Java using an array and linked list, which is another good code-related question in a programming job interview.
Stack vs Queue in Java
In this article, we will compare Stack vs Queue based upon their differences in behavior and how they are implemented and used in Java programming language.In one word, the difference between Stack and Queue comes in how they consume elements, In Stack, we remove the most recently added element, while in Queue we remove least recently added element.
Before seeing some more differences between Stack and Queue data structure, let's see some similarity between them, this will help to understand their differences better.
1) Both Stack and Queue are built on top of basic data structures like an array or linked list. Since both Stack and Queue can be bounded and unbounded, it makes sense to use an array for bounded stack and queue and may be linked list (it suits problem domain) for an unbounded queue.
2) The Java Collection API contains an implementation of both stack and queue data structure. It has a class called java.util.Stack which represents Stack and then it has a Queue interface, with a couple of implementations e.g. BlockingQueue, LinkedList, and PriorityQueue.
Now let's see differences between Stack and Queue data structure in Java:
1) The first and major difference between Stack and Queue data structure is that Stack is LIFO(Last In First Out) data structure while Queue is FIFO (First In First out) data structure.
Before seeing some more differences between Stack and Queue data structure, let's see some similarity between them, this will help to understand their differences better.
1) Both Stack and Queue are built on top of basic data structures like an array or linked list. Since both Stack and Queue can be bounded and unbounded, it makes sense to use an array for bounded stack and queue and may be linked list (it suits problem domain) for an unbounded queue.
2) The Java Collection API contains an implementation of both stack and queue data structure. It has a class called java.util.Stack which represents Stack and then it has a Queue interface, with a couple of implementations e.g. BlockingQueue, LinkedList, and PriorityQueue.
Now let's see differences between Stack and Queue data structure in Java:
1) The first and major difference between Stack and Queue data structure is that Stack is LIFO(Last In First Out) data structure while Queue is FIFO (First In First out) data structure.
So if you have a requirement where elements are processed in the order they are generated or put into Queue, you should use a Queue implementation, which supports FIFO ordering, but if you need to work with the most recently added entry, Stack would be the right data structure.
2) Key operation supported by any Stack implementation are push() and pop() which is used to add and retrieve an element from Stack, worth noting is that pop() not only retrieves element but also removes it from Stack.
2) Key operation supported by any Stack implementation are push() and pop() which is used to add and retrieve an element from Stack, worth noting is that pop() not only retrieves element but also removes it from Stack.
The key operation for Queue data structure in Java is offer() and poll(), which is used to add an object into Queue and retrieve an object from the head of Queue.
Though Queue also supports add(Object o)and remove(Object o) operation, inherited from Collection, there is a difference between them. Collection method throws Exception, while Queue methods return special values e.g. null, in exceptional cases.
For example offer() return false, if it's not able to insert an element into Queue, while add() throws a RuntimeException when it fails to add an element into Queue. Similarly poll() returns null if the queue is empty, while the remove method throws an unchecked exception.
Though Queue also supports add(Object o)and remove(Object o) operation, inherited from Collection, there is a difference between them. Collection method throws Exception, while Queue methods return special values e.g. null, in exceptional cases.
For example offer() return false, if it's not able to insert an element into Queue, while add() throws a RuntimeException when it fails to add an element into Queue. Similarly poll() returns null if the queue is empty, while the remove method throws an unchecked exception.
Since null is used as a special value, it's worth noting that Queue implementation generally doesn't allow null, but LinkedList is an exception, which does allow nulls.
3) Elements or Objects are added at the top of the Stack, but they are enquired at the different end, head and tail, in the case of a queue. Adding an element into Queue is also referred to as enqueue operation and removing an element is referred to as dequeue operation.
3) Elements or Objects are added at the top of the Stack, but they are enquired at the different end, head and tail, in the case of a queue. Adding an element into Queue is also referred to as enqueue operation and removing an element is referred to as dequeue operation.
The Head and tail of the Queue are also referred to as the front and rear of the queue. insertion takes place at the rear end, while deletion takes place at the opposite end e.g. front end. You can also read a good book on data structure and algorithms like the Introduction to Algorithms 4th Edition to learn more about different data structures and algorithms.
4) The Stack data structure is a natural recursive data structure and suits well for recursive problems e.g. implementing pre-order, post-order, and in-order traversal of the binary tree, while Queue is a sequential data structure and can be used to provide order in processing.
4) The Stack data structure is a natural recursive data structure and suits well for recursive problems e.g. implementing pre-order, post-order, and in-order traversal of the binary tree, while Queue is a sequential data structure and can be used to provide order in processing.
One example of this is a producer-consumer pattern, where a shared queue is used for data exchange between producer and consumer threads.
5) An example of using Stack data structure is reversing a String in Java, you can reverse a String by simply putting each character from String into Stack and once you finished, start popping them up. Since Stack is LIFO data structure, you will retrieve letters in reverse order.
A good example of Queue is a producer-consumer problem, in which the producer produces and consumer consumes the item. This problem also helps to understand BlockingQueue, which is a relatively new concurrent utility, which can simplify producer-consumer designs in concurrent programs.
5) An example of using Stack data structure is reversing a String in Java, you can reverse a String by simply putting each character from String into Stack and once you finished, start popping them up. Since Stack is LIFO data structure, you will retrieve letters in reverse order.
A good example of Queue is a producer-consumer problem, in which the producer produces and consumer consumes the item. This problem also helps to understand BlockingQueue, which is a relatively new concurrent utility, which can simplify producer-consumer designs in concurrent programs.
See here to learn more about how to solve producer consumer problems using BlockingQueue in Java. Another typical use of Stack is in the evaluation of the expression and converting infix to postfix notation.
As someone has rightly said that a picture is worth of 1000 words, here are two diagrams which helps you understand the difference between Stack and Queue more clearly
That's all on the difference between Stack and Queue data structure in Java. By the way, don't confuse between Stack and Heap memory with Stack and Queue, in that post, we have compared different memories in the Java platform, and here our focus is on different data structures and collection classes.
Though Stack is commonly used to store method invocation and local variable data, in terms of memory it is just a different area.
Apart from knowing the differences between these two crucial data structures, I would suggest practicing some stack and queue based exercises e.g. implementing Stack and Queue in Java using both array and linked list, adding and deleting elements from Stack and Queue, writing a unit test for Stack and Queue implementation, etc.
Apart from knowing the differences between these two crucial data structures, I would suggest practicing some stack and queue based exercises e.g. implementing Stack and Queue in Java using both array and linked list, adding and deleting elements from Stack and Queue, writing a unit test for Stack and Queue implementation, etc.
That will not only improve your Java programming skill but also your knowledge of data structure and how they work. If you are preparing for programming job interviews, you can also check Cracking the Coding Interview book for more of such exercises.
Related Data Structure and Algorithm Interview Questions from Javarevisited Blog
Thanks for reading this interview question. If you like this article, then please share it with your friends and colleagues, if you have any feedback or suggestions then please drop a comment.
Related Data Structure and Algorithm Interview Questions from Javarevisited Blog
- Difference between array and linked list data structure? (answer)
- Difference between a binary tree and a binary search tree? (answer)
- How to reverse a linked list in Java using iteration and recursion? (solution)
- How to reverse an array in place in Java? (solution)
- How to find all permutations of a String in Java? (solution)
- How to reverse a String in place in Java? (solution)
- How to remove duplicate elements from an array without using Collections? (solution)
- Top 5 Books on Data Structure and Algorithms for Java Developers (books)
- Top 5 books on Programming/Coding Interviews (list)
Thanks for reading this interview question. If you like this article, then please share it with your friends and colleagues, if you have any feedback or suggestions then please drop a comment.












1 comment :
Hi, thank you for the tutorial. Do you have a link for the actual implementations of java stacks and queues? I can't seem to get a good tutorial anywhere.
Cheers,
George
Post a Comment