The linked list is one of the most common and essential data structure and that's why you would frequently find linked list based coding questions on interviews. The range of questions can be from simple questions like finding the length of a linked list to very difficult like merging two sorted linked lists. Nevertheless, the point is that you should be familiar with linked list data structure and must know how to perform basics task in the linked list e.g. adding or removing nodes from a linked list, traversing order linked list and implementing linked list in your choice of programming language like Java, C++, C, or Python.
These linked list coding problems are not only good for coding interviews point of view but also very useful in learning programming. You should try to solve this problem yourselves, before looking at the solution to get the full benefit of them.
A linked list is nothing but a collection of nodes, where each node contains a value and pointer to the next node in the list. This structure allows you to create a chain of nodes that are scattered through different memory areas, which is in stark contrast to the array, where elements always stay in the adjacent and contiguous memory location.
The first node in the linked list is called head while the last node is called the tail. There is also two types of linked list, singly-linked list and doubly linked list. The singly linked list allows you to traverse in the only forward direction, but doubly linked list allows you to traverse in both forward and backward direction.
In order to find an element in a linked list, you need to traverse the linked list and compare each node value to the given value, this makes it an O(n) operation, not ideal when you need to frequently search, but the linked list is great for adding and removing nodes from the start and end because you just need to change one link and you don't need to shift elements like an array.
Also, basic knowledge of essential data structure is also very important and that's why I suggest all Java programmers join a comprehensive Data Structure and Algorithms course like Data Structures and Algorithms: Deep Dive Using Java on Udemy to fill the gaps in your understanding.
1. How to find the middle element of a singly linked list in one pass? (solution)
You should clarify what does mean by one pass in this question. If Interviewer says that you cannot loop twice and you just have to use one loop, then you can use the two pointer approach to solving this problem. In the two pointer approach, you have two pointers, fast and slow.
These linked list coding problems are not only good for coding interviews point of view but also very useful in learning programming. You should try to solve this problem yourselves, before looking at the solution to get the full benefit of them.
A linked list is nothing but a collection of nodes, where each node contains a value and pointer to the next node in the list. This structure allows you to create a chain of nodes that are scattered through different memory areas, which is in stark contrast to the array, where elements always stay in the adjacent and contiguous memory location.
The first node in the linked list is called head while the last node is called the tail. There is also two types of linked list, singly-linked list and doubly linked list. The singly linked list allows you to traverse in the only forward direction, but doubly linked list allows you to traverse in both forward and backward direction.
In order to find an element in a linked list, you need to traverse the linked list and compare each node value to the given value, this makes it an O(n) operation, not ideal when you need to frequently search, but the linked list is great for adding and removing nodes from the start and end because you just need to change one link and you don't need to shift elements like an array.
Also, basic knowledge of essential data structure is also very important and that's why I suggest all Java programmers join a comprehensive Data Structure and Algorithms course like Data Structures and Algorithms: Deep Dive Using Java on Udemy to fill the gaps in your understanding.
30 Linked list Interview Questions for Java Programmers
Here is my collection of some of the frequently asked linked list based coding interview questions. I am not sharing solution but you will find the solution of many articles in this blog itself, wherever possible have given links to the solution, and at some places I have also given hints to solve the problem by yourself.1. How to find the middle element of a singly linked list in one pass? (solution)
You should clarify what does mean by one pass in this question. If Interviewer says that you cannot loop twice and you just have to use one loop, then you can use the two pointer approach to solving this problem. In the two pointer approach, you have two pointers, fast and slow.
In each step, the fast pointer moves two nodes, while slow pointer just steps one node. So, when fast pointer will point to the last node i.e. where the next node is null, the slow pointer will be pointing to the middle node of the linked list.
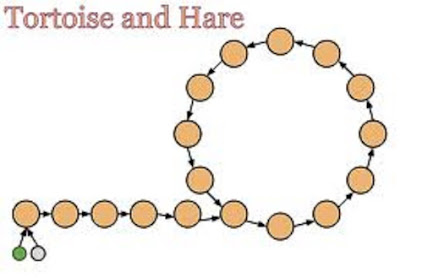
2. How to check if linked list contains loop in Java? How to find the starting node of the loop (solution)
This is another interesting linked list problem which can be solved using the two pointer approach discussed in the first question. This is also known as tortoise and hare algorithm. Basically, you have two pointers fast and slow and they move with different speed i.e. fast moves 2 notes in each iteration and slow moves one node.
2. How to check if linked list contains loop in Java? How to find the starting node of the loop (solution)
This is another interesting linked list problem which can be solved using the two pointer approach discussed in the first question. This is also known as tortoise and hare algorithm. Basically, you have two pointers fast and slow and they move with different speed i.e. fast moves 2 notes in each iteration and slow moves one node.
If linked list contains cycle then at some point in time, both fast and slow pointer will meet and point to the same node, if this didn't happen and one of the pointer reaches the end of linked list means linked list doesn't contain any loop.
3. How to reverse a linked list in Java? (solution)
This is probably the most popular linked list interview question, which is asked to both junior programmers with 2 to 3 years of experience and senior developers containing 4 to 6 years of experience.
Some of you may think this is the simplest of linked list problem but when you actually go doing it, you will be stuck and many places. The simplest approach to solving this problem is by using recursion because linked list is a recursive data structure as shown in the solution article.
4. How to reverse a singly linked list without recursion in Java? (solution)
The previously linked list interview question becomes even more challenging when the interviewer asked you to solve the problem without recursion. you need to keep reversing links on the node until you reach the end, which will then become new head.
5. How would you remove a node from a doubly-linked list? (solution)
This is one of the frequently asked linked list interview questions, mostly asked freshers and computer science college graduates. In order to remove a node from the doubly linked list, you need to go through that node and then change the links so that it points to the next node.
4. How to reverse a singly linked list without recursion in Java? (solution)
The previously linked list interview question becomes even more challenging when the interviewer asked you to solve the problem without recursion. you need to keep reversing links on the node until you reach the end, which will then become new head.
5. How would you remove a node from a doubly-linked list? (solution)
This is one of the frequently asked linked list interview questions, mostly asked freshers and computer science college graduates. In order to remove a node from the doubly linked list, you need to go through that node and then change the links so that it points to the next node.
Removing nodes from head and tail is easy in the linked list but removing a node from the middle of the linked list requires you to travel to the node hence take O(n) time.
If you want to learn more about basic operations on linked list data structure, please read a good book on Data Structure and Algorithms like Introduction to Algorithms book by Thomas H. Cormen. 4th Edition of this book is now available which is much better than previous edition.
6. Write a Program to convert a binary tree into a doubly-linked list? (solution)
This problem is the opposite of question 25 where you need to write a program to convert a double linked list to the balanced binary tree. The left and right pointers in nodes of a binary tree will be used as previous and next pointers respectively in converted doubly-linked ist.
6. Write a Program to convert a binary tree into a doubly-linked list? (solution)
This problem is the opposite of question 25 where you need to write a program to convert a double linked list to the balanced binary tree. The left and right pointers in nodes of a binary tree will be used as previous and next pointers respectively in converted doubly-linked ist.
The order of nodes in the doubly linked list must be the same as Inorder of the given Binary Tree. The first node of Inorder traversal (leftmost node in the binary tree) must be the head node of the doubly linked list.
7. How to remove duplicate nodes in an unsorted linked list? (solution)
This problem is similar earlier problems related to String and arrays i.e. removing duplicate elements in an array (see) or removing duplicate characters from given String (see here). You need to write a program to remove all duplicate nodes from an unsorted linked list in Java.
7. How to remove duplicate nodes in an unsorted linked list? (solution)
This problem is similar earlier problems related to String and arrays i.e. removing duplicate elements in an array (see) or removing duplicate characters from given String (see here). You need to write a program to remove all duplicate nodes from an unsorted linked list in Java.
For example if the linked list is 22->21->22->31->41->23->21 then your program should convert the list to 22->21->31->41->23. This question is also given in the famous Cracking the Coding Interview book so you can look at their solution as well.
8. Write a recursive method to determine whether a linked list is sorted in descending order or not? If it's sorted then return true otherwise return false. (solution)
8. How to find the length of a singly linked list in Java? (solution)
This is one of the easiest linked list questions you can expect in an interview. That's why it is often asked on telephonic interviews. In order to find the length of the linked list, you can iterate over the linked list and keep a count of nodes until you reach the end of the linked list where the next node will be null. The value of the counter is the length of the linked list.
9. Write code to print out the data stored in each node in a singly linked list? (solution)
This is another simplest question which just tests whether you know linked list traversal or not. You can get the value from the node by accessing its value property, you just need to traverse through linked list, access each node, and print value.
10. Write a Program to print a linked list in reverse order? E.g. Print linked list from tail to head? (solution)
You can print nodes of linked list in reverse order by using Stack data structure in two steps:
Step 1: Traverse the linked list from the head and put the value of each node into Stack until you reach the last node. This will take O(n) time.
Step 2: Pop the elements out from the stack and print. This will take O(1) time.
Input: 1->2->3
Output: 3 2 1
11. How to delete a node from a Singly linked list in O(1) time? (solution)
You can delete a node from a linked list by first traversing through that node and then changing the link, I mean current node will point to the new next node.
12. How to find the Kth node from the end in a singly linked list? (solution)
This is one of the tricky but frequently asked linked list questions. Some of you may be wondering how do you find kth node from end, singly linked list can only traverse in one direction and that is forward then how do you count nodes from the end?
Well, you don't have to, you can still move forward and count nodes from the end? Actually, that's the trick. You can use two pointers to find the Nth node from the end in a singly linked list. They are known as fast and slow points.
You start slow pointer when the fast pointer reaches the Kth node from start like if you have to find 3rdnode from the end then you start slow pointer when the fast pointer reaches to the 3rd node. This way, when your fast pointer reaches to the end, your slow pointer will be on the 3rd node from the end.
13. How do you find the first intersection node of two linked lists in Java? (solution)
14. Write a method in Java to sort a given linked list? Also, write Unit tests. (solution)
15. How do you merge two sorted lists into a single sorted linked list? (solution)
Suppose you are given two linked list L1 and L2, you need to write a method to create linked list L3 as shown in the following diagram
16. How to swap every two nodes in a linked list? (solution)
8. Write a recursive method to determine whether a linked list is sorted in descending order or not? If it's sorted then return true otherwise return false. (solution)
8. How to find the length of a singly linked list in Java? (solution)
This is one of the easiest linked list questions you can expect in an interview. That's why it is often asked on telephonic interviews. In order to find the length of the linked list, you can iterate over the linked list and keep a count of nodes until you reach the end of the linked list where the next node will be null. The value of the counter is the length of the linked list.
9. Write code to print out the data stored in each node in a singly linked list? (solution)
This is another simplest question which just tests whether you know linked list traversal or not. You can get the value from the node by accessing its value property, you just need to traverse through linked list, access each node, and print value.
10. Write a Program to print a linked list in reverse order? E.g. Print linked list from tail to head? (solution)
You can print nodes of linked list in reverse order by using Stack data structure in two steps:
Step 1: Traverse the linked list from the head and put the value of each node into Stack until you reach the last node. This will take O(n) time.
Step 2: Pop the elements out from the stack and print. This will take O(1) time.
Input: 1->2->3
Output: 3 2 1
11. How to delete a node from a Singly linked list in O(1) time? (solution)
You can delete a node from a linked list by first traversing through that node and then changing the link, I mean current node will point to the new next node.
12. How to find the Kth node from the end in a singly linked list? (solution)
This is one of the tricky but frequently asked linked list questions. Some of you may be wondering how do you find kth node from end, singly linked list can only traverse in one direction and that is forward then how do you count nodes from the end?
Well, you don't have to, you can still move forward and count nodes from the end? Actually, that's the trick. You can use two pointers to find the Nth node from the end in a singly linked list. They are known as fast and slow points.
You start slow pointer when the fast pointer reaches the Kth node from start like if you have to find 3rdnode from the end then you start slow pointer when the fast pointer reaches to the 3rd node. This way, when your fast pointer reaches to the end, your slow pointer will be on the 3rd node from the end.
13. How do you find the first intersection node of two linked lists in Java? (solution)
14. Write a method in Java to sort a given linked list? Also, write Unit tests. (solution)
15. How do you merge two sorted lists into a single sorted linked list? (solution)
Suppose you are given two linked list L1 and L2, you need to write a method to create linked list L3 as shown in the following diagram
16. How to swap every two nodes in a linked list? (solution)
17. How to find the frequency of a given number in a Linked List? (solution)
18. How to delete alternate nodes of a Linked List? (solution)
You are given a Singly Linked List. Starting from the second node delete all alternate nodes of it. For example, if the given linked list is 1->4->8->10->15 then your function should convert it to 1->8->15
19. What is the difference between an array and a linked list in Java? (answer)
This is one of the frequently asked linked list questions on programming job interviews. There is much difference between an array and linked list but the most important is how they are stored into the memory location.
Array stores elements at the adjacent memory location, while linked list stores them at scattered, which means searching is easy in an array and difficult in linked list but adding and removing an element from start and end is easy in linked list. See here for more differences between array and linked list.
20. Difference between singly and doubly linked list in Java? (answer)
The key difference between a single and double linked list data structure in java is that singly linked list only contains a pointer to next node, which means you can only traverse in one direction i.e. forward, but the doubly linked list contains two points, both previous and next nodes, hence you can traverse to both forward and backward direction.
21. How to implement a linked list using Generics in Java? (solution)
It's not easy to implement a linked using generics in Java, especially if have not written any parametric or generic class, but it's a good exercise to get familiar with both linked list data structure as well as generics in Java.
21. How to insert a node at the beginning of the list? (solution)
Inserting a node at the beginning of the list is probably the easiest of all operations. Let’s talk about what is involved here referring to the diagram above. This involves creating a new node (with the new data, say int 10), making its link point to the current first node pointed to by head (data value 2) and lasting changing head to point to this new node. Simple, right
22. How to insert a node at the end of the list? (solution)
This case is a little bit more evolved. If you have a tail pointer, it is as easy as inserting at the beginning of the list. If you do not have a tail pointer, you will have to create the new node, traverse the list till you reach the end (i.e. the next pointer is NULL) and then make that last node’s next pointer point to the new node.
23. How do you traverse a linked list in Java? (solution)
There are multiple ways to traverse a linked list in Java e.g. you can use traditional for, while, or do-while loop and go through the linked list until you reach the end of the linked list. Alternatively, you can use enhanced for loop of Java 1.5 or Iterator to traverse through a linked list in Java. From JDK 8 onwards, you can also use java.util.stream.Stream for traversing a linked list.
24. How do you find the sum of two linked list using Stack in Java? (solution)
This is a relatively difficult linked questions when you compare this to reversing a linked list or adding/removing elements from the linked list. In order to calculate the sum of linked list, you calculate the sum of values held at nodes in the same position, for example, you add values at first node on both the linked list to find the first node of resultant linked list.
If the length of both linked list is not same then you only add elements from shorter linked list and just copy values for remaining nodes from the long list.
25. How do you convert a sorted doubly linked list to a balanced binary search tree in Java? (solution)
This is one of the difficult linked list questions you will find on interviews. You need to write a program to convert a given doubly Linked, which is sorted in ascending order to construct a Balanced Binary Search Tree which has same the values as the given doubly linked list.
25. How do you convert a sorted doubly linked list to a balanced binary search tree in Java? (solution)
This is one of the difficult linked list questions you will find on interviews. You need to write a program to convert a given doubly Linked, which is sorted in ascending order to construct a Balanced Binary Search Tree which has same the values as the given doubly linked list.
The challenge is usually increased by putting a restriction to construct the BST in-place i.e. no new node should be allocated for tree conversion)
Input: A Doubly linked list 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
Output: A balanced binary search tree BST
40
/ \
20 60
/ \ / \
10 30 40 70
26. How do you calculate the sum of two linked list using recursion in Java? (solution)
This is another interesting linked list based algorithm question for Java programmers. You cannot use the java.util.LinkdList class but you have to write your own linked list implementation in Java to solve this problem.
27. How to implement LRU cache in Java using linked list? (solution)
An LRU cache is the cache where you remove least recently used an element when the cache is full or about to fill. It's relatively easy in Java if you are allowed to use one of the Collection class e.g. you can use a LinkedHashMap to implement LRU cache in Java, but you should also prepare how you can use a doubly linked list to create an LRU cache.
28. How to add an element in the middle of a linked list in Java? (solution)
One of the easier linked list interview question. In order to add a node into the middle, you need to first find the middle element, which is one problem we have seen in first few questions. After that it just changing the links to add a node, no shifting is required.
Input: A Doubly linked list 10 20 30 40 50 60 70
Output: A balanced binary search tree BST
40
/ \
20 60
/ \ / \
10 30 40 70
26. How do you calculate the sum of two linked list using recursion in Java? (solution)
This is another interesting linked list based algorithm question for Java programmers. You cannot use the java.util.LinkdList class but you have to write your own linked list implementation in Java to solve this problem.
27. How to implement LRU cache in Java using linked list? (solution)
An LRU cache is the cache where you remove least recently used an element when the cache is full or about to fill. It's relatively easy in Java if you are allowed to use one of the Collection class e.g. you can use a LinkedHashMap to implement LRU cache in Java, but you should also prepare how you can use a doubly linked list to create an LRU cache.
28. How to add an element in the middle of a linked list in Java? (solution)
One of the easier linked list interview question. In order to add a node into the middle, you need to first find the middle element, which is one problem we have seen in first few questions. After that it just changing the links to add a node, no shifting is required.
This is also an exercise from Bruce Eckel's Thinking in Java book, a good one to learn both Java and Programming.
29. How do you reverse every alternate k nodes of a Linked List in Java? (solution)
This is another difficult linked list algorithm question which is mostly asked to experience programmers e.g. programmer having 3 to 6 years of experience. You have been given a singly linked list and you need to write a function to reverse every alternate k nodes (where k is an input to the function) in an efficient way. You also need to calculate the time and space complexity of your algorithm.
Example:
Inputs: 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9->NULL and k = 3
Output: 3->2->1->4->5->6->9->8->7->NULL.
30. How do you add two numbers represented using the linked list in Java? (solution)
You have given two numbers represented by two linked lists, write a function that returns the sum of these two lists. The sum list is linked list representation of the addition of two input numbers.
29. How do you reverse every alternate k nodes of a Linked List in Java? (solution)
This is another difficult linked list algorithm question which is mostly asked to experience programmers e.g. programmer having 3 to 6 years of experience. You have been given a singly linked list and you need to write a function to reverse every alternate k nodes (where k is an input to the function) in an efficient way. You also need to calculate the time and space complexity of your algorithm.
Example:
Inputs: 1->2->3->4->5->6->7->8->9->NULL and k = 3
Output: 3->2->1->4->5->6->9->8->7->NULL.
30. How do you add two numbers represented using the linked list in Java? (solution)
You have given two numbers represented by two linked lists, write a function that returns the sum of these two lists. The sum list is linked list representation of the addition of two input numbers.
There are two restrictions to solve this problem i.e. you cannot modify the lists and you are not allowed to use explicit extra space. You can use recursion to solve this problem.
Input:
First List: 1->2->3 // represents number 123
Second List: 9->9->9 // represents number 999
Output
Resultant list: 1->1->2->2 // represents number 1122
That's all about some of the frequently asked linked list based coding questions from Programming Interviews. As I said, the linked list is one of the essential data structures and you should have a good command over it, especially if you are preparing for Google or Amazon job interviews.
Input:
First List: 1->2->3 // represents number 123
Second List: 9->9->9 // represents number 999
Output
Resultant list: 1->1->2->2 // represents number 1122
That's all about some of the frequently asked linked list based coding questions from Programming Interviews. As I said, the linked list is one of the essential data structures and you should have a good command over it, especially if you are preparing for Google or Amazon job interviews.
Once you solved these linked list problems, you can try solving questions given in Algorithm Design Manual book by Steven S. Skiena. They are tougher but can really improve your data structure and algorithm skills.
Other Resources for Programming/Coding Job interviews
- Top 30 Array-based Coding Interview Questions (see)
- Top 20 String-based Algorithm Interview Questions (practice)
- Top 100 Data Structure and Algorithm Questions from Java Interviews (practice)
- 5 Books to Prepare Programming/Coding Interviews (list)
- 5 Data Structure and Algorithm books for Java Programmers (list)
- 20 System Design Interview Questions (design questions)
- 50 Database and SQL Questions (database questions)
- 40 OOP Interview Questions with answers (OOP questions)
- 75 Programming Interview Questions with answers (programming questions)
- 10 Dynamic Programming Interview Questions (dynamic programming)
- 25 Recursion Interview Questions with answers (recursion questions)
Thanks for reading this article so far. If you like this article then please share with your friends and colleagues. If you have any suggestion or feedback then please drop a comment. If you got any other interesting linked list interview questions, feel free to share.
And lastly which one is your favorite linked list based problem from coding interviews? finding Kth element from last, checking if linked list has loop, or reversing a singly linked list without recursion?














1 comment :
Great questions, thanks for sharing but can you please share answers or solutions for questions like
16. How to swap every two nodes in a linked list? (solution)
17. How to find the frequency of a given number in a Linked List? (solution)
Recently I was also asked about find the common element in two unsorted linked list? do you know how to do that?
Post a Comment